:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/adductor-magnus/g1fZHNB0jDn4LZRRPUp8Q_GnYu3kkn8bt9ifsgt3Ug_sSyqxhtwKC_M._adductor_magnus_NN_1.png)
Adductor magnus Origin, insertion, innervation, action Kenhub
This video covers the anatomy of the adductor magnus muscle: origins, insertion, innervation and function. Watch our in-depth 3D animation video about the fu.
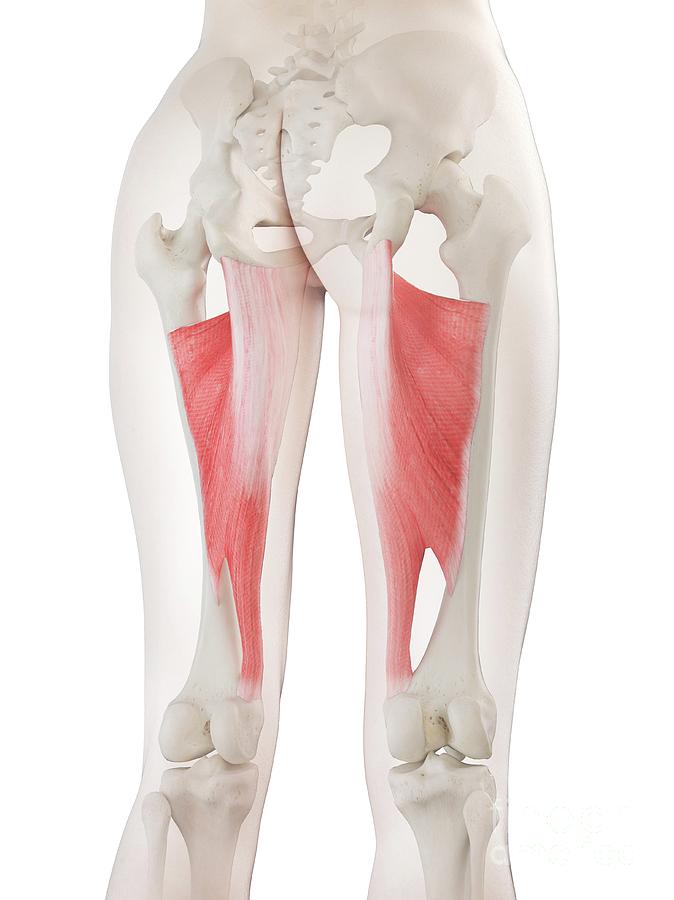
Adductor Magnus Muscle Photograph by Sebastian Kaulitzki/science Photo Library Pixels
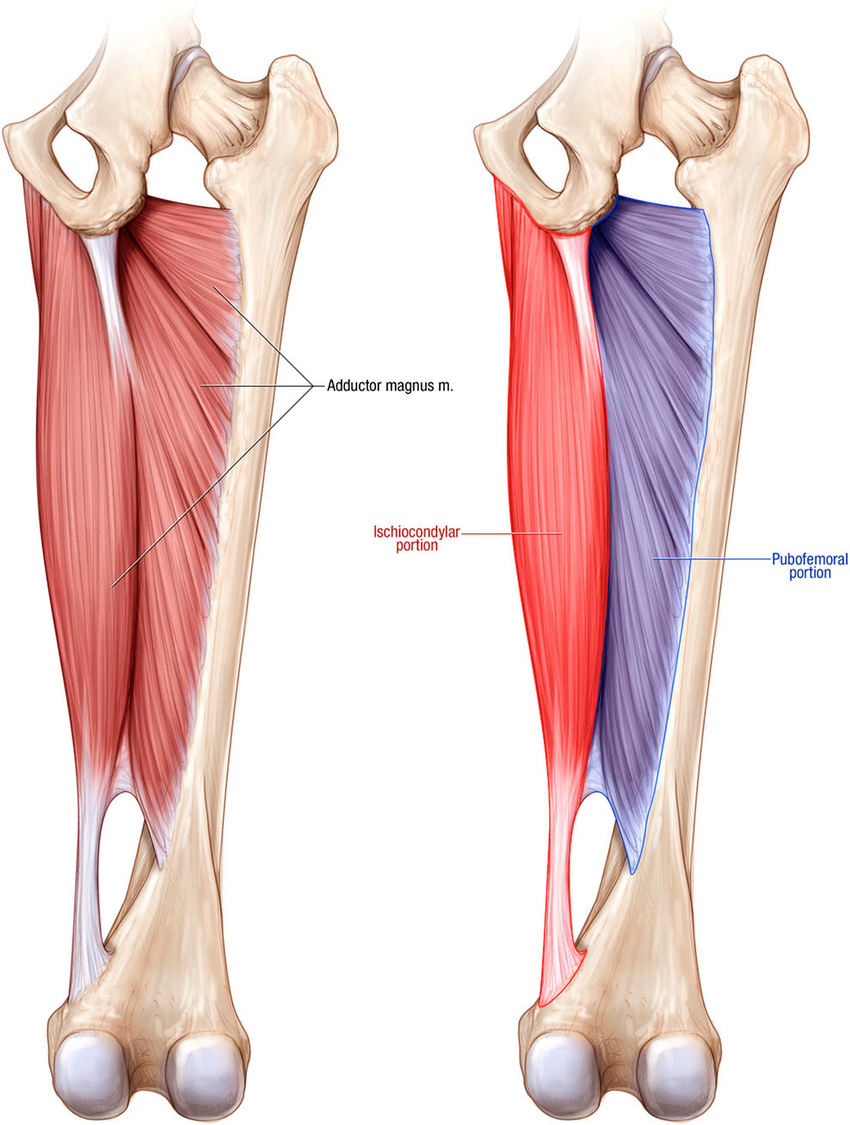
The adductor magnus muscle is a massive triangular muscle that extends over the entire medial side of the thigh. It is a composite muscle consisting of two parts, the adductor part and the hamstring part, also called the ischiocondylar part. The adductor part: arises from the outer surface of the inferior pubic ramus of pubic bone and the.
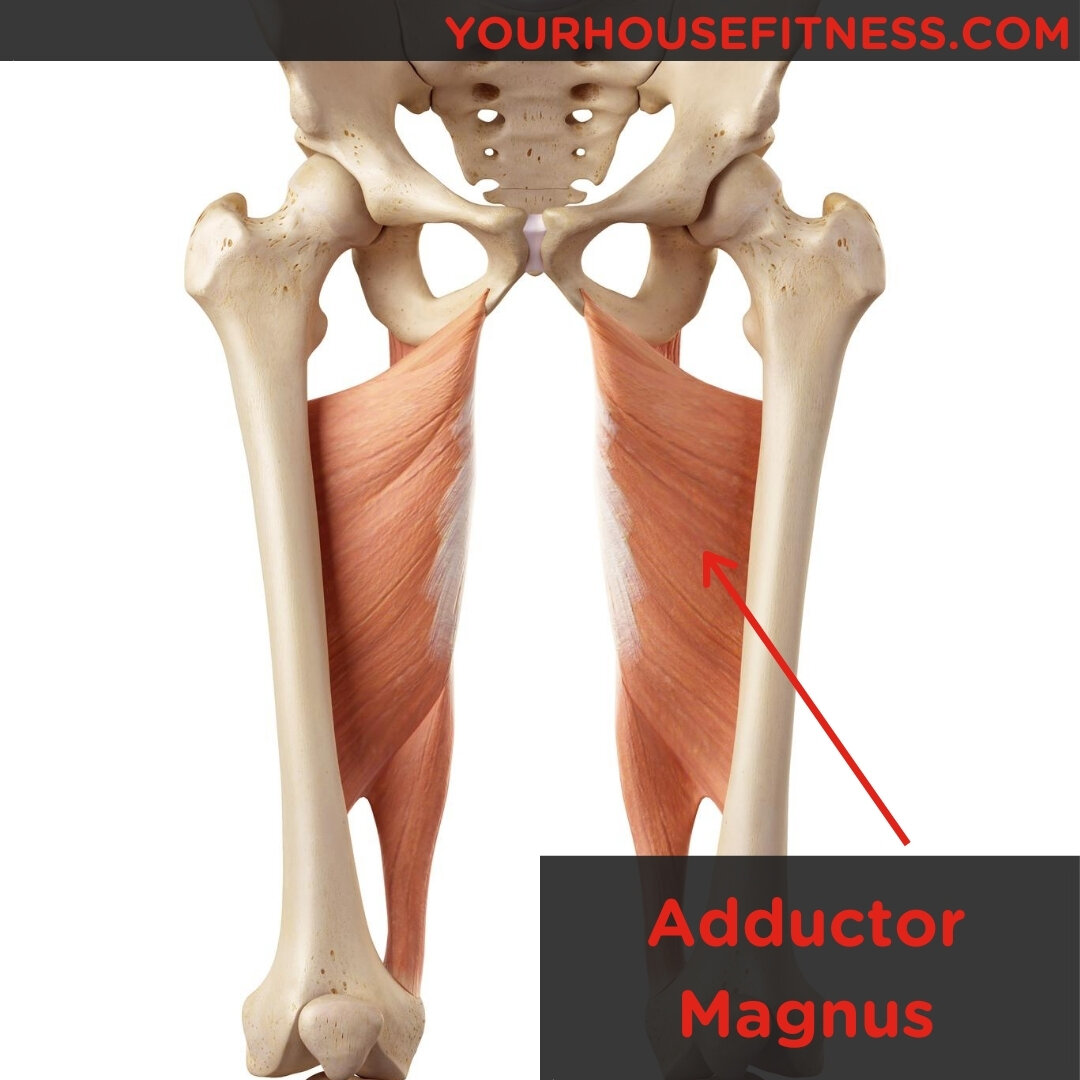
Muscle Breakdown Adductor Magnus
Origin: Pubis, tuberosity of the ischium Insertion: Femur Artery: Obturator artery Nerve: Posterior branch of obturator nerve (adductor) and sciatic nerve (hamstring) Action: Adduction of hip Description: The Adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh. It arises from a small part of the inferior ramus of the pubis, from the inferior ramus of the.
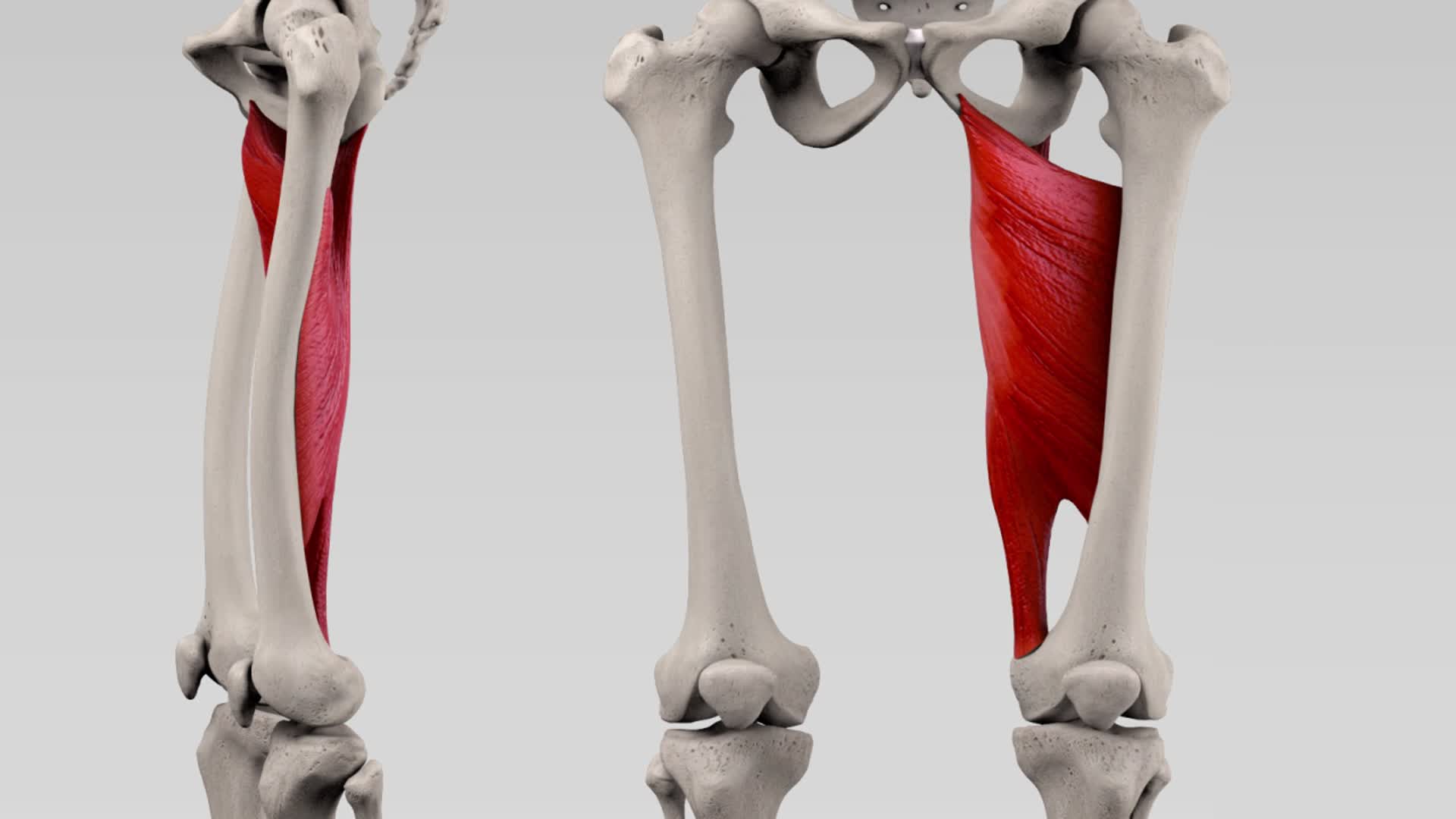
Musculus adductor magnus DocCheck
Adductor Magnus. Origin: Inferior pubic ramus, ischial ramus, and inferolateral area of ischial tuberosity. Insertion: Gluteal tuberosity of femur, medial lip of linea aspera, medial supracondylar ridge, and adductor tubercle. Action: Powerful thigh adductor; superior horizontal fibers also help flex the thigh, while vertical fibers help extend.
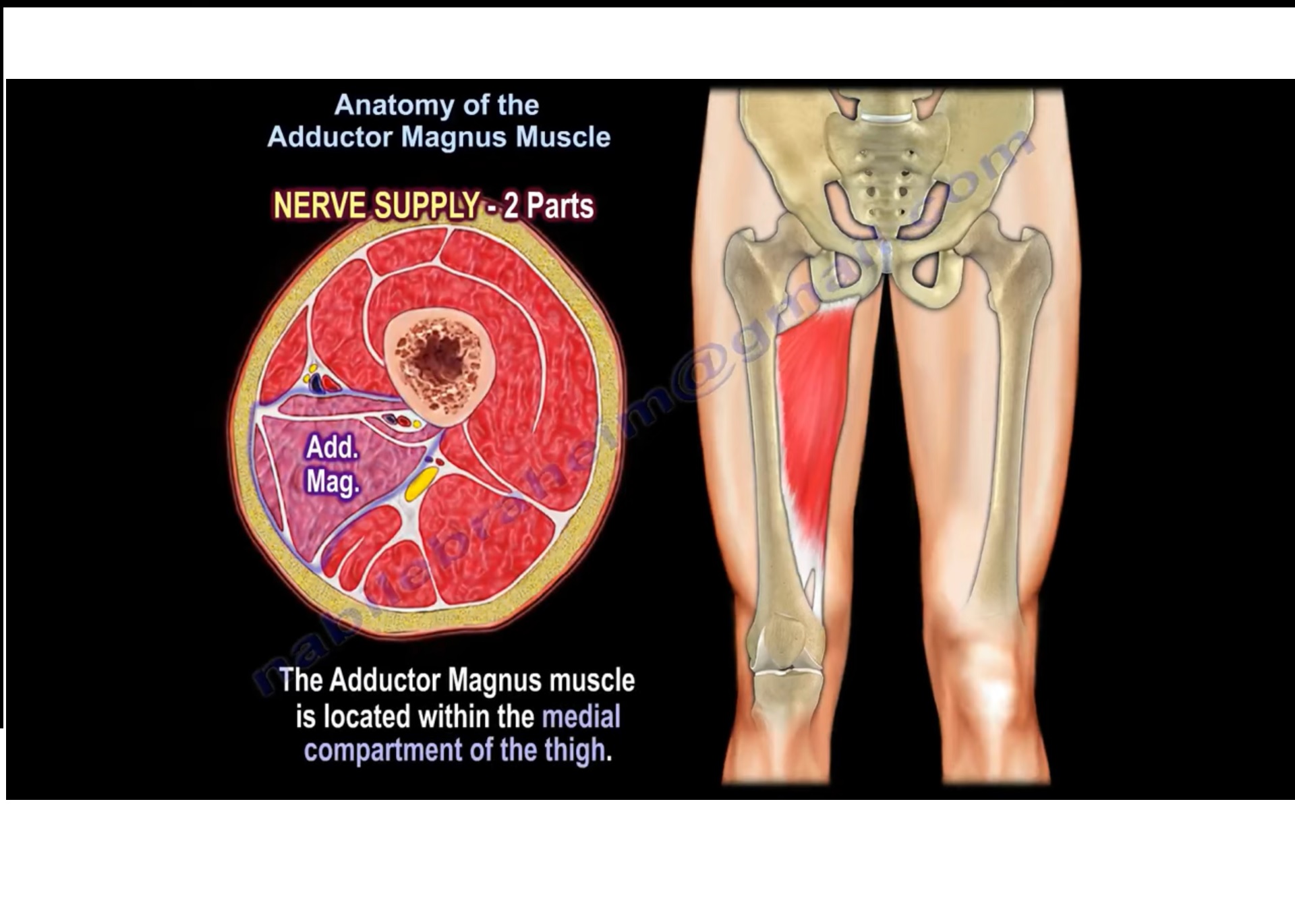
Anatomy of the Adductor Magnus Muscle —
Adductor Magnus. The adductor magnus is the largest muscle in the medial compartment of the thigh. It is comprised of two parts - an adductor component and a hamstring component. Attachments. Adductor - Originates from the inferior rami of the pubis and the rami of ischium, attaches to the linea aspera of the femur.
3 Exercises For Adductor Mobility — ONI Wellington Personal Training Studio
This article describes our surgical technique for management of a rare acute proximal adductor magnus avulsion. Hip adduction is accomplished through coordinated effort of the adductor magnus, brevis, and longus and the obturator externus and pectineus muscles. Because of the proximity of their origins on the pubis and ischium, the adductor.
Adductor Magnus Muscle Photograph by Sebastian Kaulitzki/science Photo Library Fine Art America
Adductor Magnus, the largest single contributor to the adductor group of the medial thigh, is a broad functioning muscle with significant contribution to not only adduction, but extension and rotation at the hip. The aim of this review is to investigate the terminology, anatomical and functional characteristics of AM, particularly its role as an extensor and stabiliser at the hip.
Pictures Of Adductor Magnus Tendons
Adductor Magnus Footprint Anatomic and Dimensional Characteristics. Mean AM ischial footprint height (AP) was 12.1 ± 2.9 mm (range, 8.9-17.8 mm). The mean width (ML) was 17.3 ± 7.1 mm (range, 6.5-27.5 mm). With all tendons reflected from their origins, the mean distance between the AM ischial footprint and the most medial aspect of the.

The adductor magnus muscle
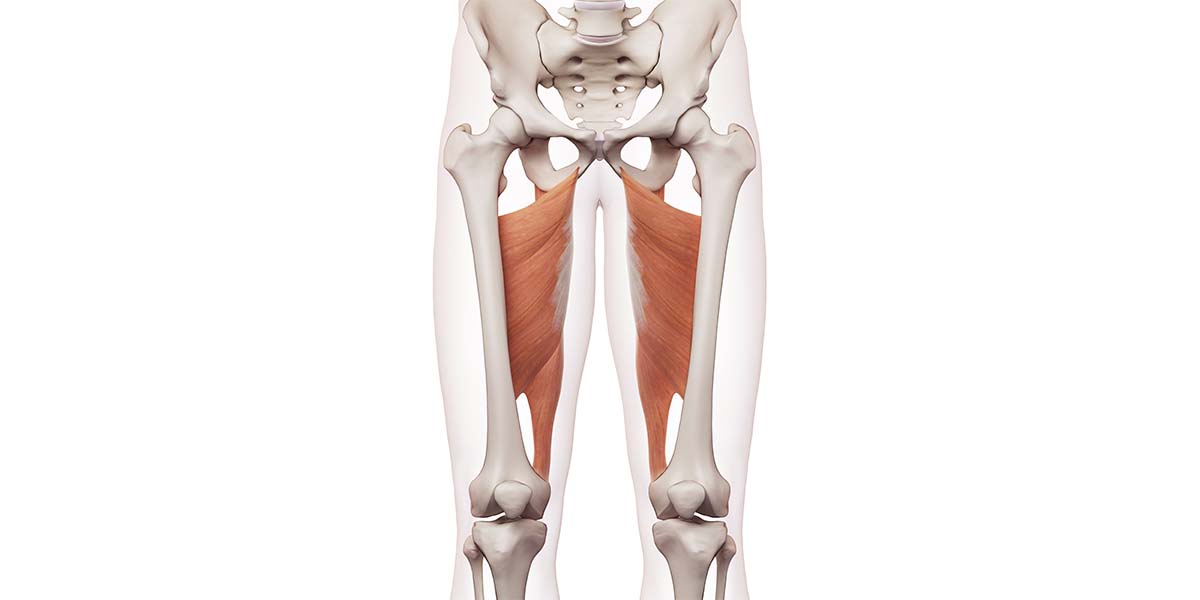
Adductor magnus. On the medial side (closest to the middle) of the thigh, the adductor magnus muscle creates the shape of a large triangle. As an adductor, it contracts and pulls the hip towards.
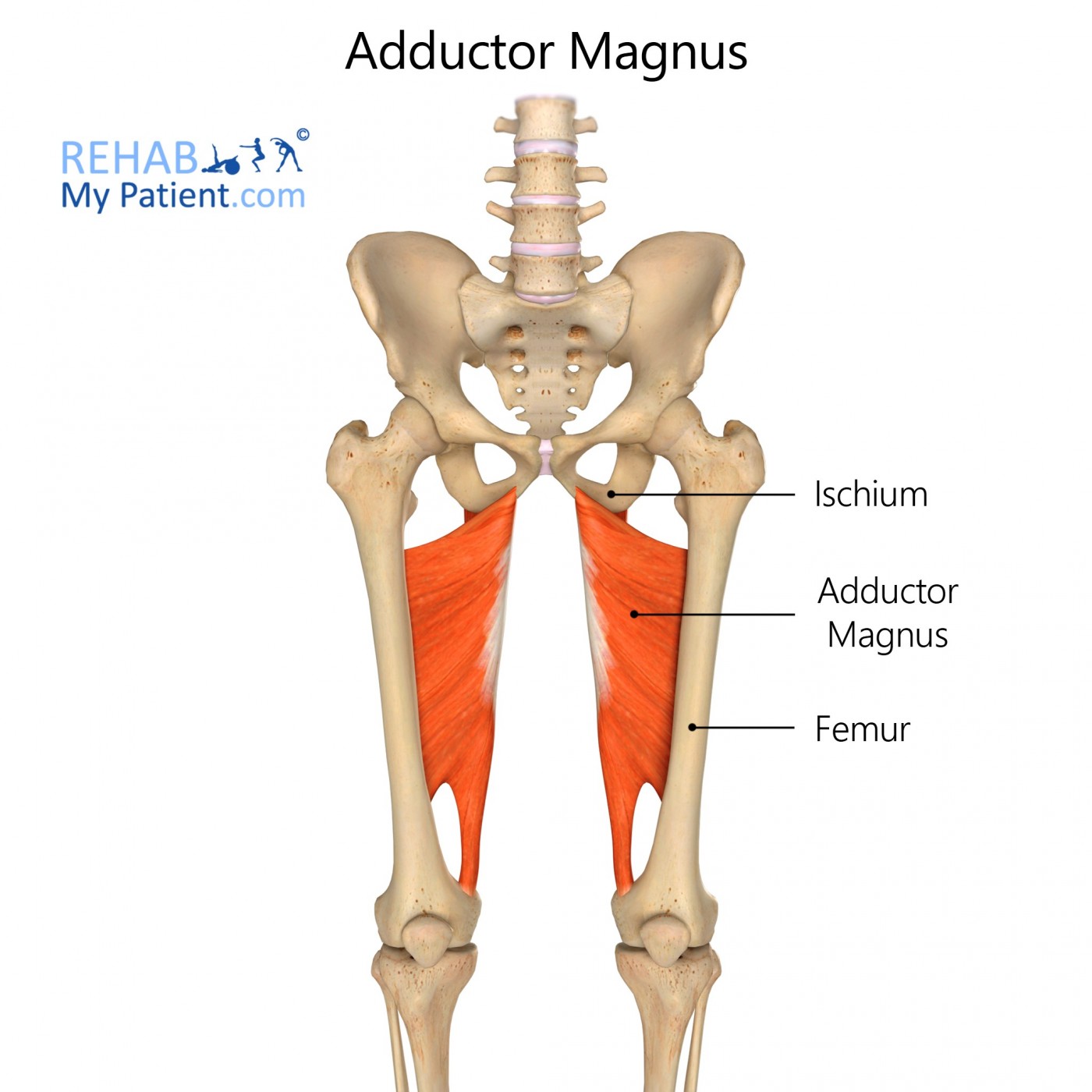
Adductor Magnus Rehab My Patient
The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh . It consists of two parts. The portion which arises from the ischiopubic ramus (a small part of the inferior ramus of the pubis, and the inferior ramus of the ischium) is called the pubofemoral portion, adductor portion, or adductor minimus, and the.

Adductor Magnus Learn Muscles
The Adductor Magnus muscle is one of hip adductors. The adductor magnus is the largest, most powerful and the most complex, of the adductor group. This muscle is complex in that part derived from the fact that it divides into an adductor (pubofemoral) portion and a hamstring (ischiocondylar) portion. It lies deep to the adductor brevis and the.
Adductor Magnus Anatomie und Funktion
Adductor magnus is supplied by the. obturator artery. femoral artery. medial femoral circumflex. direct and perforating branches of the deep femoral artery. Obturator artery. arises from internal iliac artery in pelvis. bifurcates in medial thigh into two branches. anterior branch - pectineus, obturator externus, adductor muscles and gracilis.

The Adductor Magnus; Not just for adduction anymore... — The Gait Guys
Adductor magnus is the largest and deepest of the adductor group. The adductor muscles are a group of five muscles that primarily function to adduct the femur at the hip joint. But they also generally assist with flexion of the hip joint. However, as you'll see below, this muscle also assists in hip extension. Yes, you read that correctly.

Adductor magnus Anatomy Orthobullets
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The adductor magnus muscle is the largest and deepest of the muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh. Like the adductor longus and brevis muscles, the adductor magnus is a triangular or fan-shaped muscle anchored by its apex to the pelvis and attached by its expanded base to the femur.

Adductor Magnus Pain Groin, Pelvic and Thigh Pain The Wellness Digest
Adductor Magnus. - origin: - posterior fibers: ischial tuberosity; - anterior fibers: ramus of ischium and pubis; - insertion: - from a line extending from the greater trochanter along linea aspera, medial suprcondylar line and adductor tubercle on medial condyle of femur; - action: - adduction of the thigh at the hip;

The adductor magnus stock illustration. Illustration of upper 57547850
Adductor magnus (the largest muscle in the group) These muscles adduct the thigh and stabilize the pelvis, maintaining its balance during walking. The adductor magnus is the largest and most posterior of the medial thigh compartment muscles (see Image. Medial Compartment of the Thigh). Some consider it the most powerful and most complex of the.